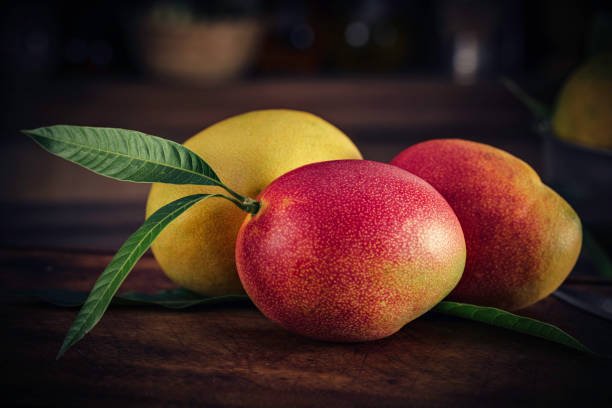
Mango: Smart Eating for Weight, Heart, and Eye Health

What is Mango and What is Its Scientific Name?
Mango is a delicious, juicy, and aromatic tropical fruit, loved for its sweet flavor and rich, golden-yellow flesh. It grows on large evergreen trees. Mango belongs to the Anacardiaceae family, and its scientific name is Mangifera indica.
History and Origin of Mango
The mango has a fascinating history stretching back over 4,000 years. It is believed to have originated in the region of present-day India, Myanmar, and Bangladesh. Ancient Indian writings and legends celebrate the mango as a symbol of prosperity and love. From South Asia, mangoes spread to Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Americas through travelers, traders, and colonial expansion. Today, mango is cherished worldwide as the “King of Fruits.”

How Many Categories of Mango Are There?
There are over 1,000 varieties of mangoes in the world! Mangoes are categorized by color, size, flavor, and fiber content. Some are sweet, others slightly tangy. Popular categories include Alphonso, Himsagar, Kesar, Tommy Atkins, Kent, Ataulfo, and Palmer. Some are good for eating fresh, while others are best for juicing or pickling.
Nutritional Value of 100 Grams of Mango (All Nutrients)
A 100-gram serving of ripe mango contains:
- Calories: 60 kcal
- Water: 83%
- Protein: 0.8 g
- Carbohydrates: 15 g
- Fat: 0.4 g
- Vitamins:
- Minerals:
- Antioxidants: Beta-carotene, mangiferin, quercetin and polyphenols
Why Is Eating Mango Beneficial?
Mangoes are low in fat and sodium, but high in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They provide energy, boost immunity, and are a delightful way to stay hydrated in summer. Mangoes are also rich in natural sugars, making them a sweet treat without artificial additives.
What Are the Health Benefits of Eating Mango?
- Strengthens Immunity: High vitamin C and A content boost the immune system.
- Improves Digestion: Enzymes and fiber promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation.
- Promotes Eye Health: Beta-carotene supports vision and eye health.
- Enhances Skin and Hair: Vitamins and antioxidants support glowing skin and strong hair.
- Good for the Heart: Potassium and magnesium help control blood pressure and support heart health.
- May Lower Cancer Risk: Mangiferin and polyphenols have potential anti-cancer properties.
How Much Mango Should You Eat Per Day?
One medium-sized mango (about 200 grams) or one cup of sliced mango per day is a healthy amount for most adults. It can be part of your daily fruit intake, but moderation is key due to its natural sugar content.
How to Store Mango?
- At Room Temperature: Keep unripe mangoes at room temperature to ripen.
- Refrigeration: Once ripe, mangoes should be refrigerated and consumed within a few days.
- Avoid Cutting Until Ready: Cut mangoes spoil quickly, so slice them just before eating.
When Is the Best Time to Eat Mango?
Mangoes can be enjoyed any time of the day. Many love having them as a refreshing snack on hot afternoons, as part of breakfast, or in smoothies and desserts. Avoid eating too many mangoes late at night, especially for those with sensitive digestion.
Does Eating Mango Cause Weight Gain or Loss?
Mangoes are moderate in calories and fat-free. Eaten in moderation, they do not cause weight gain and can be part of a healthy diet. Their fiber helps you feel full, which may actually support weight management.
Which Mango Is Best for Diabetics?
Diabetics should choose less ripe mangoes and eat in moderation, as ripe mangoes are quite sweet. Pairing mango with protein or healthy fats can help control blood sugar spikes.
Which Diseases or Conditions Benefit from Eating Mango?
Mangoes are particularly beneficial for:
- Boosting immunity
- Improving digestion
- Supporting eye and skin health
- Reducing risk of heart disease
- Aiding in constipation and dehydration
- Providing antioxidants for cell protection
In Which Countries or Regions Are Mangoes Most Popular?
Mango is most popular in South Asia (India, Bangladesh, Pakistan), Southeast Asia, and is also widely loved in the Middle East, Africa, Latin America, and the Caribbean. In the West, mango consumption is rapidly rising.
When Does Mango Demand and Price Increase or Decrease?
Mango demand and prices peak during the summer months (April to July) when the fruit is in season. Prices tend to be lower during the harvest and higher at the beginning and end of the season, or when supply is limited.
Which Country Leads in Commercial Mango Production?
India is the world’s largest mango producer, followed by China, Thailand, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Mexico. India accounts for almost half of the world’s mango supply.
Conclusion
Mango is more than just a fruit—it’s a celebration of flavor, culture, and nutrition. With its rich taste, vibrant color, and impressive health benefits, mango truly lives up to its title as the “King of Fruits.” Enjoy mangoes in moderation throughout the season for a delicious boost to your health and happiness.
Calcium & Sources: How to Boost Your Daily Intake

What Is Calcium?
Calcium is a vital mineral essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, supporting nerve function, muscle contraction, and blood clotting. It is the most abundant mineral in the human body, making up about 1.5% of total body weight. Without adequate calcium, our body cannot perform these critical functions properly.
What Is Calcium Made Of?
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. In the human body, it exists in the form of calcium salts within bones and teeth, providing structure and strength. It also circulates in the bloodstream, participating in various physiological processes.
Where Is Calcium Found?
Calcium is naturally found in many foods, especially dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt. It is also present in leafy green vegetables (like spinach and kale), almonds, sesame seeds, fish (like salmon and sardines), and fortified foods such as cereals and plant-based milk. Additionally, calcium supplements are available for those who need extra intake.
Does Calcium Make Our Bones and Teeth Strong?
Absolutely! Calcium is the primary building block of bones and teeth. About 99% of the body’s calcium is stored in these structures, giving them strength and density. Adequate calcium intake during childhood, adolescence, and early adulthood is crucial for developing a strong skeletal system.
How Important Is Calcium?
Calcium is extremely important for overall health. It supports bone density, prevents osteoporosis, helps in muscle function, facilitates nerve signal transmission, and is vital for blood clotting. Maintaining optimal calcium levels is essential for both children and adults to prevent health issues.
What Happens If Calcium Is Deficient?
A deficiency in calcium can lead to weakened bones, increased risk of fractures, and conditions like osteoporosis. In children, calcium deficiency can impair growth and development. Symptoms like muscle cramps, numbness, and abnormal heart rhythms may also appear with severe deficiency.
What Are the Signs of Too Little or Too Much Calcium?
Low calcium symptoms include muscle cramps, tingling in fingers, fatigue, and brittle bones. Excess calcium, often from supplements, can cause kidney stones, constipation, and interfere with the absorption of other minerals. It may also lead to abnormal heart rhythms.
How Can You Fill the Calcium Gap?
To address calcium deficiency, include calcium-rich foods in your diet, such as dairy, leafy greens, and fortified products. Supplements can be taken if recommended by a healthcare provider. Additionally, vitamin D helps calcium absorption, so ensure adequate sunlight exposure or supplements if needed.
How Is Calcium Made or Produced?
Calcium is a naturally occurring mineral obtained from rocks and minerals like limestone, which is processed to produce calcium carbonate and other supplements used in food fortification and medicine.
Is Calcium a Natural Ingredient?
Yes, calcium is a naturally occurring mineral found in the earth’s crust and in many foods. It has been part of the human diet for thousands of years, primarily through dairy and plant-based sources.
Is Calcium Suitable for All Ages?
Yes! Calcium is essential for all age groups. Children need it for growth, teenagers for bone development, adults for maintaining bone density, and older adults to prevent osteoporosis. Adequate calcium intake benefits everyone.
Is Calcium Beneficial for Children?
Absolutely! Calcium is crucial for children’s growth, bone development, and overall health. Adequate calcium intake during childhood and adolescence builds a strong skeletal foundation for lifelong health.
Conclusion
Calcium is an indispensable mineral vital for maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and overall bodily functions. Ensuring sufficient calcium intake through diet or supplements, along with vitamin D, helps prevent deficiency-related health issues like osteoporosis and supports growth and development at every age.
FAQs:(Frequently Asked Questions)
Is Calcium Harmful for Diabetes?
Calcium itself is not harmful for diabetics and may even support overall health. However, excessive calcium intake from supplements should be avoided, as it can cause other health issues. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Are There Alternatives to Calcium?
Yes, plant-based sources like kale, broccoli, almonds, and fortified plant milks are good alternatives. Vitamin D also plays a critical role in calcium absorption, so maintaining optimal vitamin D levels is essential.
Does Calcium Help in Weight Loss?
Calcium alone does not directly cause weight loss. However, some studies suggest that adequate calcium intake may help regulate appetite and fat metabolism, supporting a healthy weight when combined with proper diet and exercise.